Did you know that EVs can work for their drivers and the environment even when they aren’t being driven? That’s because we now have vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology.
(Image Source: Toka Energy)
V2G tech is one component in the overall effort to achieve a zero-carbon future. A challenge of many renewable energy sources is that the power they produce must either be used immediately or stored. V2G helps mitigate climate change by allowing our energy system to balance more renewable energy.
Stationary energy storages are increasingly common, and these big power banks are a good way to store energy from large solar power plants. Pump stations are also common, where water is pumped up and down to store energy. EV batteries are considered the most cost-efficient energy storage since they require no additional hardware investment.
Here are ten things you should know about V2G.
1. What is V2G technology?
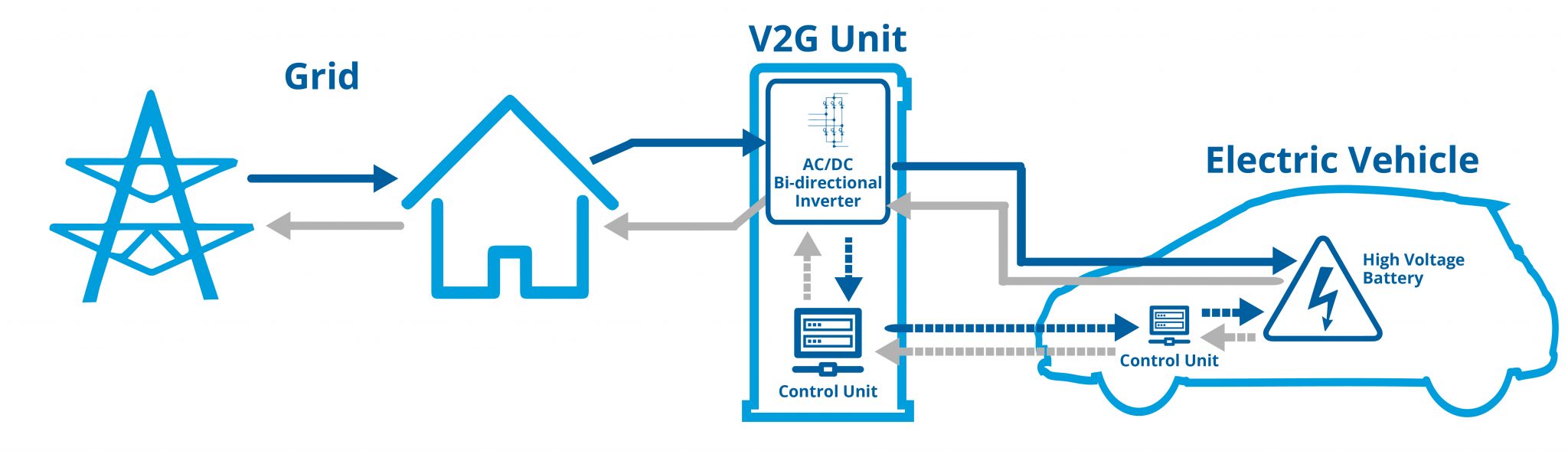
Vehicle-to-grid technology feeds unused energy stored in an EV battery to the national grid. In addition to helping boost grid supply during peak demand, V2G can be a source of revenue for EV owners.
EV owners must use a DC smart charger specially configured for two-way transmission. They can either charge their car from the grid or sell stored electrical energy back to the grid by bypassing the car’s unidirectional onboard charger. The charger decides when to import and export power from the EV at scheduled times that are best for the owner and the grid.
Maximum V2G charging power is around 10 kW, just enough for home or workplace charging. In the future, more comprehensive charging solutions will apply.
2. What does “grid balancing” mean?
Grid balancing makes sure that electricity is available from the power grid when it’s needed. When the grid is not balanced, utilities must purchase electricity on the open market or suffer power shortages.
Conventional grid balancing involves ramping up power plants that primarily use fossil fuels. This increases fuel consumption and emissions. Using energy stored in batteries is a far better alternative in terms of both environmental impact and cost.
With increasing frequency, America’s power grid is experiencing surges, shortages, brownouts, and blackouts, which are expected to continue due in part to EV charging. By 2030, the U.S. will have as many as 35 million EVs. That’s a lot of demand on the power grid and a lot of stored battery power that we could direct toward lessening the incidence of grid brownouts and blackouts.
3. How does V2G work?
EV owners want enough energy in their car batteries to drive when they want to go somewhere, but the average car is parked about 90 percent of the time. V2G puts that unused power to good use.
By leaving the parked car plugged into a V2G-capable smart charger, the EV owner can participate in grid balancing while their car sits idle. Their EV can sell power to the grid while parked at work during peak daytime demand and recharge at home overnight when rates are usually at their lowest.
4. What Are The Types of V2G?
There are three models or types of V2G: Unidirectional, bidirectional local, and bidirectional:
- With unidirectional V2G (also known as V1G), the energy flow is only from the grid to your EV. You can charge your battery only when there is a surplus of energy produced in renewable energy power plants. EVs are used to balance the grid frequency and improve energy stability.
- Bidirectional local V2G feeds only local energy needs at your home or commercial building. There are two bidirectional local V2G types: vehicle-to-home (V2H) and vehicle-to-building (V2B).
- Bidirectional V2G addresses the entire grid and is what most people mean when talking about V2G technology. Depending on the need, this model stores energy in your EV battery and draws from it.
The latter two are also called V2X (see question 10, below).
5. What are the key benefits of V2G?
V2G can be a game-changer for the EV industry in several powerful ways.
- Adds stability and reduces stress for the grid
- Reduces carbon emissions by contributing clean, green energy
- Makes driving cheaper and more energy-efficient for EV owners
- Provides added value for EV owners by selling surplus energy
- Reduces total cost of fleet ownership
A smarter, stable, flexible grid supported by V2G can speed the decrease in dependence on fossil fuels and a cleaner environment.
(Image source: ElectricRate.com)
6. Does V2G work for all electric cars?
Not yet. To use V2G in its present form, the EV has to be compatible with a CHAdeMO DC connector. Nissan and Mitsubishi are the leaders in manufacturing EVs with V2G capabilities. The following are some of the models and companies that offer V2G capabilities:
- Nissan Leaf
- Ford F-Series Pickup Trucks
- Tesla
- Mitsubishi
- BMW
- Honda
7. Does V2G affect car battery life?
Some opponents claim that V2G technology reduces the lifespan of EV batteries. Most experts believe that V2G discharging, which only happens for a few minutes daily, does not affect battery life. However, experts are constantly studying the EV battery lifecycle and the impact of V2G on it.
8. How much does V2G cost?
V2G capability is estimated to add $200–$400 to the price of the vehicle. A 10-kW (Level 2) DC bi-directional EVSE unit can cost another $4,500–$5,500, which the commercial charging station is responsible for (or, in the case of private chargers, the individual EV owner or business).
9. What is vehicle-to-grid integration?
Vehicle-to-grid integration, or VGI, takes the concept of V2G a step further. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) is developing and evaluating fully integrated systems that connect EVs, charging infrastructure, buildings, power grids, renewable energy sources, and behind-the-meter storage options.
10. What is V2X?
V2X is a bidirectional charging technology that allows you to charge any object or device from your car batteries. EV battery capacity is enough to power an average home for around three days non-stop if the house uses <30 kWh of energy per day (the U.S. average). See question 4 above for more information.
Are you interested in learning more about opportunities for your business in EV Charging? Join us at the upcoming EV Charging Summit & Expo!






