Microgrids are becoming an increasingly important part of the energy landscape, as they offer several advantages over traditional grid systems. Still, we’re pretty early in the nationwide growth curve of microgrid use; they currently provide just 0.2 percent of US electricity and are primarily concentrated in Alaska, California, Georgia, Maryland, New York, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Still, anyone who takes the time to learn about the potential and benefits of microgrids will quickly understand why the future of microgrid usage is bright. Here’s everything you need to know about microgrids.
What Are Microgrids?
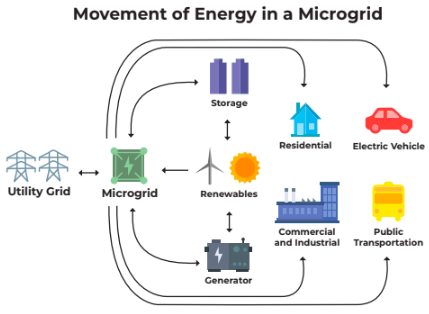
Image source: climable.org
Microgrids are local energy systems that can operate independently from the traditional grid. A microgrid typically contains a mix of generation sources (e.g., solar, wind, natural gas), storage devices (e.g., batteries), and loads (e.g., homes, businesses, and electric vehicles). Microgrids can be used to power a single building or a group of buildings, and they offer many advantages over traditional grid-connected systems.
What Role Do Microgrids Play In Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure?
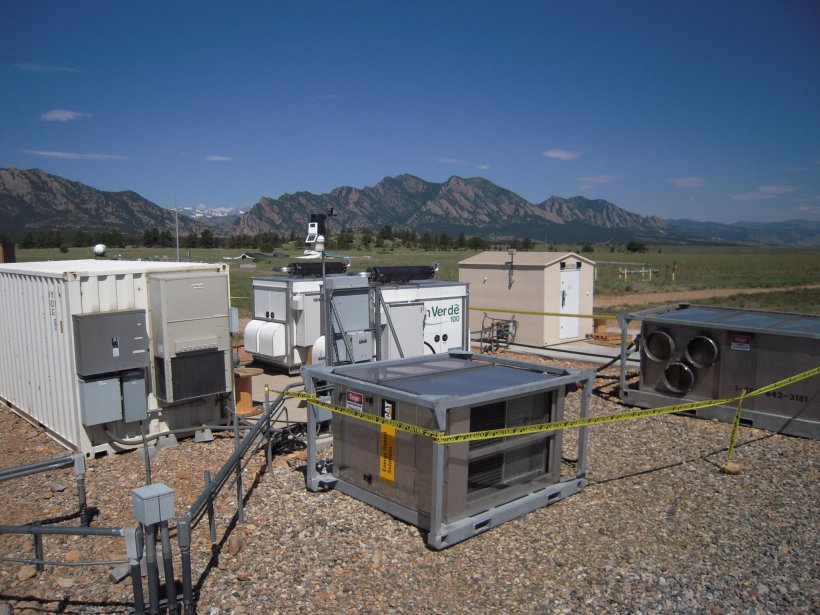

Image source: energy.gov
Microgrids play a vital role in electric vehicle charging infrastructure, providing the clean, reliable power needed to charge EVs. In addition, microgrids can help to optimize the charging process by managing when and how much power is delivered to each EV. This helps to ensure that EVs are charged efficiently and that the grid remains stable.
Challenges Facing Microgrid Expansion
Despite the many benefits of microgrids, some challenges still need to be addressed to reach their full potential. These challenges include:
Funding and Financing

Microgrids can be expensive to develop and implement, and there is a lack of funding and financing options. Microgrids require a significant investment in infrastructure; to build a microgrid, you need to purchase or lease land, install generation sources and storage devices, and connect the system to the grid. This investment can cost millions of dollars.
Technical Challenges
Some technical challenges, such as grid integration and interoperability, still need to be addressed. Grid integration refers to connecting a microgrid to the larger electric grid, made challenging by microgrids’ often remote locations. Interoperability refers to the ability of different devices and systems to work together. This is important for microgrids, as they often contain a mix of generation sources and storage devices from different manufacturers.
Regulatory Barriers
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has yet to issue regulations specifically for microgrids. Additionally, many states lack the laws or regulations to support microgrid expansion.
Top Benefits of Microgrids

Microgrids improve energy security and reliability. Because microgrids are local energy systems, they are less vulnerable to large-scale outages. In a grid outage, microgrids can operate independently. This is especially beneficial for critical loads, such as hospitals and emergency shelters.
In addition to improved energy security, microgrids also offer other benefits, such as:
Improved Resilience
Microgrids can help improve the electric grid’s resilience by providing backup power during an outage. Notably, the town of Fairfield, Connecticut, switched to a microgrid after 2011’s Hurricane Irene caused almost 1 million Connecticut homes to lose power.
Enhanced Sustainability
Microgrids can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts by integrating renewable energy sources. According to estimates from power-grid.com, microgrids can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industrial facilities by more than 60%.
Economic Development
Microgrids can spur economic development by attracting new businesses and industries to a region. For example, the Philadelphia Navy Yard now hosts one of the largest private microgrids in the United States, supporting 7.5 million feet of commercial space.
Top Players in the Space

Many companies are leading the charge in the development and deployment of microgrids. Some of the top players in this space include:
Alencon Systems
Alencon Systems is a leading provider of microgrid control systems. The company has deployed over 200 MW of microgrid capacity around the world.
Ameresco
Ameresco is an energy services company specializing in developing, financing, and implementing energy efficiency and renewable energy projects.
Concord Engineering
Concord Engineering offers microgrid engineering and consulting services. The company has worked on over 500 microgrid projects around the world.
Cummins
Cummins is a global leader in designing, manufacturing, and selling engines and generators. They also offer a range of microgrid solutions.
Eaton
Eaton develops electrical products and solutions. The company offers a range of microgrid solutions, including storage, controls, and inverters.
Generac
Generac is a top manufacturer of backup generators. Their microgrid solution integrates solar, storage, and generators.
Mesa Solutions
Mesa Solutions is a leading provider of microgrid development, financing, and implementation services. The company has worked on over 200 microgrid projects around the world.
NRG Energy
NRG Energy is an energy company that offers a range of microgrid solutions. NRG Energy has deployed over 50 MW of microgrid capacity around the world.
PowerSecure
PowerSecure also provides microgrid solutions. The company has deployed more than 300 MW of microgrid capacity worldwide.
PXiSE Energy Solutions
PXiSE Energy Solutions is an industry champion of microgrid development, financing, and implementation services, having worked on more than 500 microgrid projects around the world.
Rolls-Royce mtu
Rolls-Royce mtu manufactures engines and generators. The company also offers a range of microgrid solutions.
S and C Electric
S and C Electric is another leading provider of microgrid solutions. They’ve deployed more than 600 MW of microgrid capacity around the world.
Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric produces electrical products and solutions. The company offers a range of microgrid solutions, including storage, controls, and inverters.
Siemens
Siemens is a global leader in designing, manufacturing, and selling electrical products and solutions. Siemens also boasts a range of microgrid solutions.
Veolia
Veolia specializes in energy efficiency and renewable energy services. Veolia’s range of microgrid solutions includes storage, controls, and inverters.
Xendee
Xendee produces microgrid development software. The company has worked on more than 500 microgrid projects around the world.
The Future of Microgrids

Despite the challenges, microgrids are becoming increasingly popular and will play a significant role in our future energy system.
To learn more, check out our upcoming EV Charging Summit and Expo.






