This article will walk you through how EV charging load management works, what you should know to take the best advantage of load balancing, and the top vendors in the space.
What is EV charging load management?
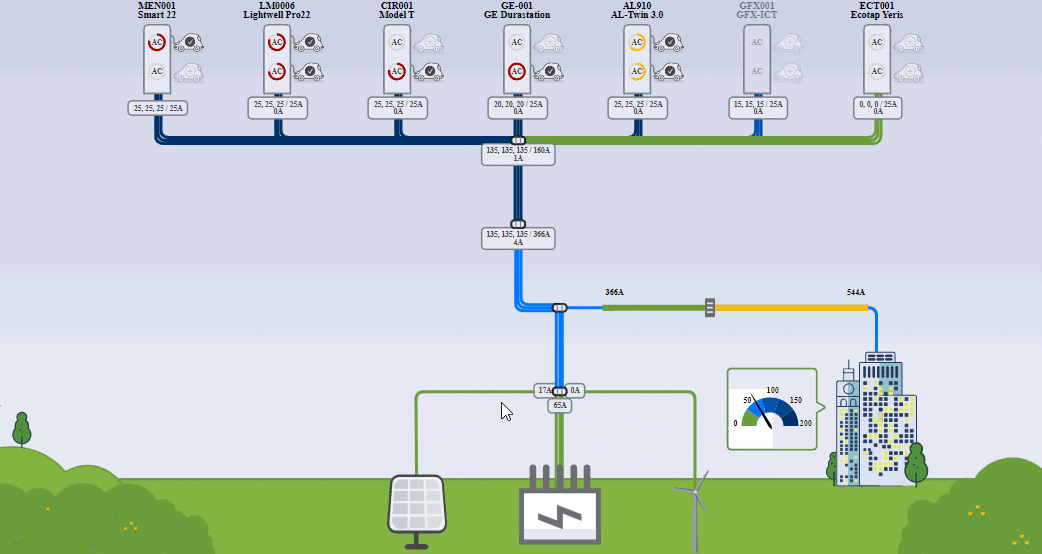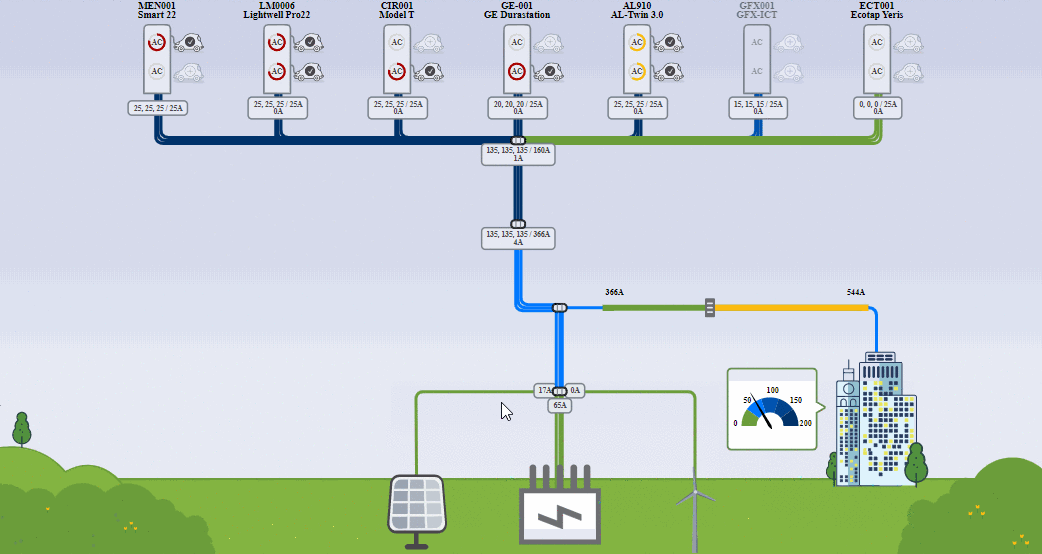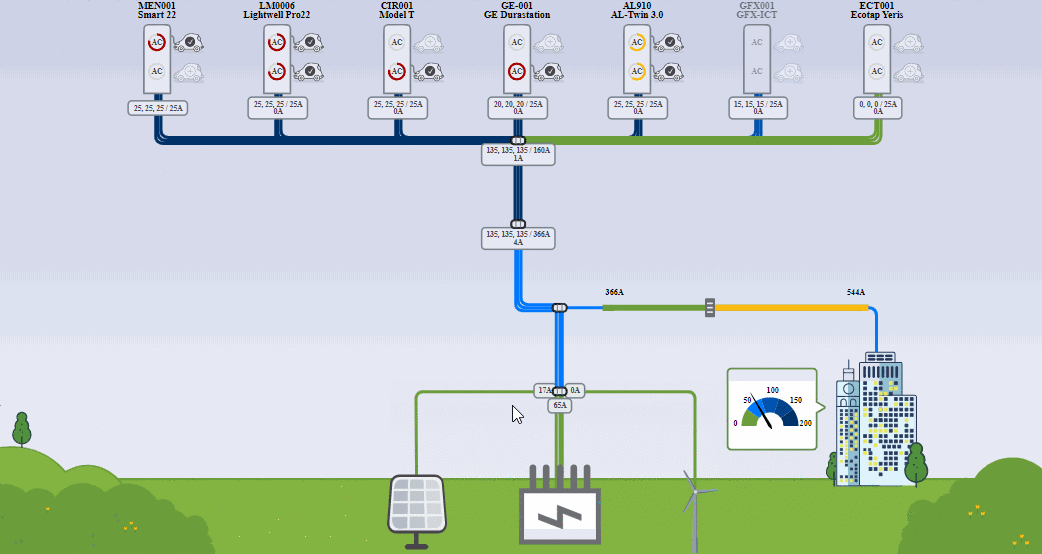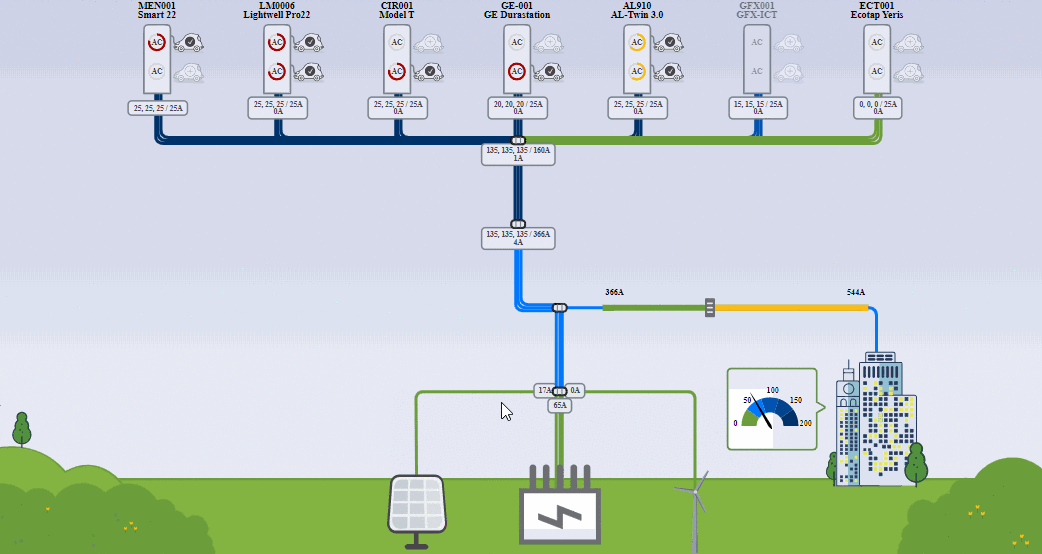
(Image source: Driivz.com)
Electric vehicle charging load management is the term for balancing the demand for energy throughout the day. Load management reduces energy usage during peak demand periods, reducing the burden on the grid. At the same time, it optimizes EV charging.
At the macro level, load management creates equilibrium among power demand across multiple sites like individual charging ports, fleet depots, residential buildings, or public parking lots.
At the micro level, load management shifts the charging session for a single charge point to a time when energy is less expensive. When cars use multiple charge points, load management balances the power to ensure that vehicles are charged efficiently.
How does EV charging load balancing work?
Load balancing systems instruct EV chargers to deliver the right amount of energy. They offset peak demand at the charging site level, in onsite battery storage, and within campuses.
EV charging load management software constantly communicates with the electricity infrastructure, charge points, and charging EVs. Well-known loan management software vendors include Picafuel, Tridens Technology, eDRV, and GreenFlux.
EV charging load balancing can be static (based on the time or day) or dynamic, where it adjusts energy consumption in real-time and redirects it to areas of greatest need. EV load balancing can react to changes, such as vehicle arrivals and peak demand, or to requirements known in advance, such as overnight charging requirements for an EV fleet.
Why should EV charging providers care about load balancing?
Load balancing maximizes charging site efficiency and customer satisfaction by ensuring that each charge point has the right amount of energy to service each vehicle. EV charging load balancing ensures that the grid can charge every car on time 24/7.
EV charging load balancing also means the charging service provider can access electricity from the grid during off-peak hours and store it onsite to meet peak customer demand without paying peak-hour rates to the utility. Load management and balancing help service providers avoid fines for taxing the grid during peak demand times.

EvoCharge iEVSE Plus 32 Amp (ImageSource: EvoCharge)
What is a charge management system?
A charge management system lets the charging site operator control how much power each station can use when multiple EVSE (electric vehicle supply equipment) units are connected to the same circuit. The chargers will automatically follow the pre-set protocol to balance electricity usage by each EVSE. By allowing charging stations to talk to each other, steady electrical current is doled to each.
What are the best load-balancing EV chargers?
Some of the better-known “smart” EV chargers featuring load-balancing capabilities include the PowerFlex EV charger, the Zappi EV charger, and the Wallbox Pulsar Plus. The Tesla Gen 3 EV charger features power-sharing technology.
How does EV load management provide power?
Load-sharing EV chargers provide stations with a steady stream of power in one of two ways: equal distribution or first-in, first-charged.
With equally distributed load sharing, each EV charger gets the same amount of electricity depending on how many amps are available and how many stations are in use. If the electrical panel provides 80 amps and four 40-amp chargers, each charger will receive an equal amount of 20 amps. The three active chargers will get 26 amps if one charger leaves.
With first-in, first-charged load sharing, power distribution to the EV chargers depends on when charging begins. Using our four 40-amp charging station example, the first station would charge its EV customer at full capacity, while the second would get what’s left. If additional power remains after the needs of the first two stations are met, the third vehicle will get that. Once the first vehicle left, its load would move to the third vehicle, and any overage would begin charging the fourth station.
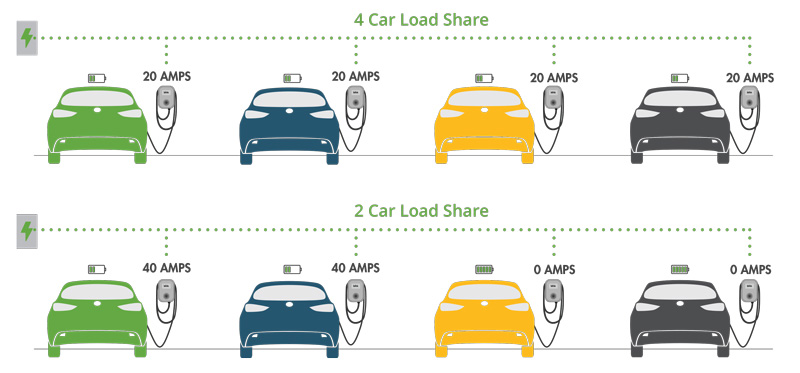
(Image Source: Blinkcharging.com)
Deciding on the best type of load sharing depends on how you want chargers to be used. Fleet managers usually want to charge all vehicles at once over a longer period, so they would use equal distribution. On the other hand, an apartment manager wants tenants to finish charging as soon as possible to make room for other tenants to use the station, so they would use first-in, first-charged.
Conclusion
Investing in load-sharing EV chargers will help you save time, money, and effort over the long haul, whether you’re planning to add multiple charging stations to your property immediately or at some other point in the foreseeable future.
Interested in learning more about EV Charging infrastructure and strategies? Join us at the upcoming EV Charging Summit and Expo!
Featured Image by senivpetro on Freepik.






